Scientific Image Gallery
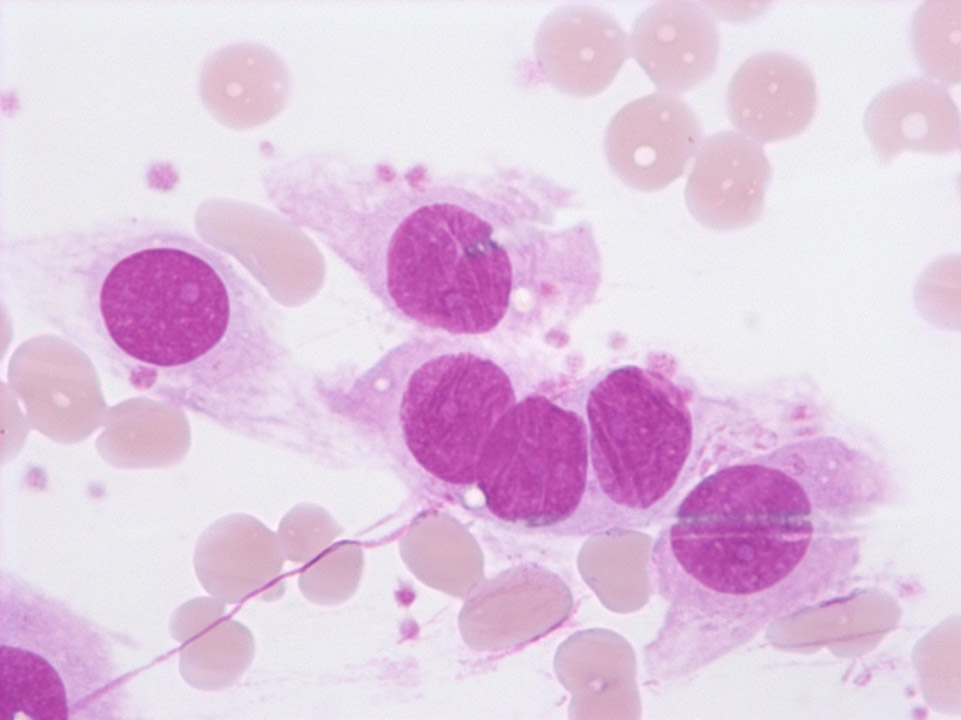
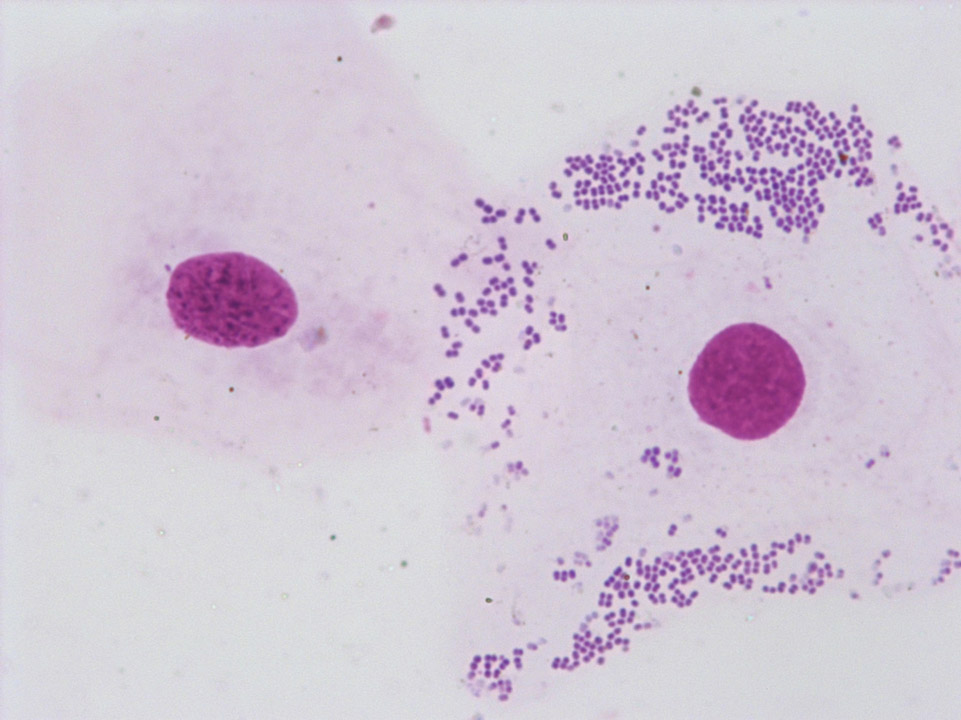
The endothelial cells are part of the vascular wall, which was damaged during venepuncture. (Blood coagulation was activated during the process: on the bottom left a fibrin fibre can be recognised.)
<p>The endothelial cells are part of the vascular wall, which was damaged during venepuncture. (Blood coagulation was activated during the process: on the bottom left a fibrin fibre can be recognised.)</p>
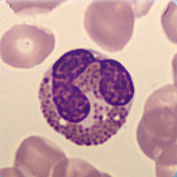
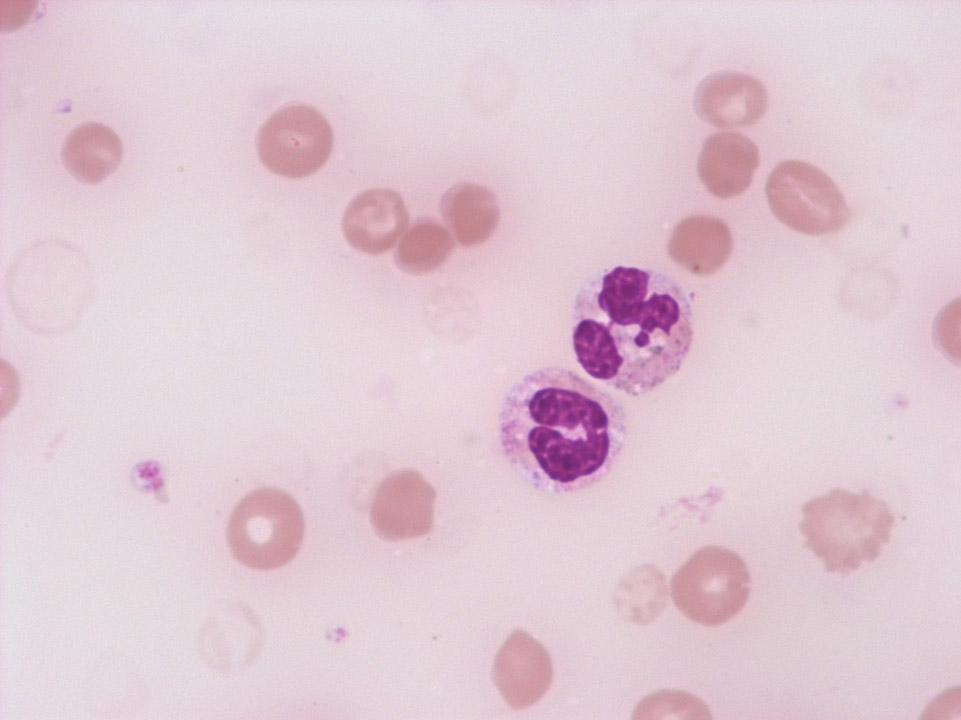
Size: 12-17 µm
Nucleus: usually bilobed with visible filament
Cytoplasm: weekly basophilic containing coarse reddish-orange granulation packing the cytoplasm
Function: Phagocytosis, chemotaxis, mortification of parasites, inhibition of mastcell degranulation, eutralization of histamine
<p>Size: 12-17 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: usually bilobed with visible filament </p> <p>Cytoplasm: weekly basophilic containing coarse reddish-orange granulation packing the cytoplasm </p> <p>Function: Phagocytosis, chemotaxis, mortification of parasites, inhibition of mastcell degranulation, eutralization of histamine</p>
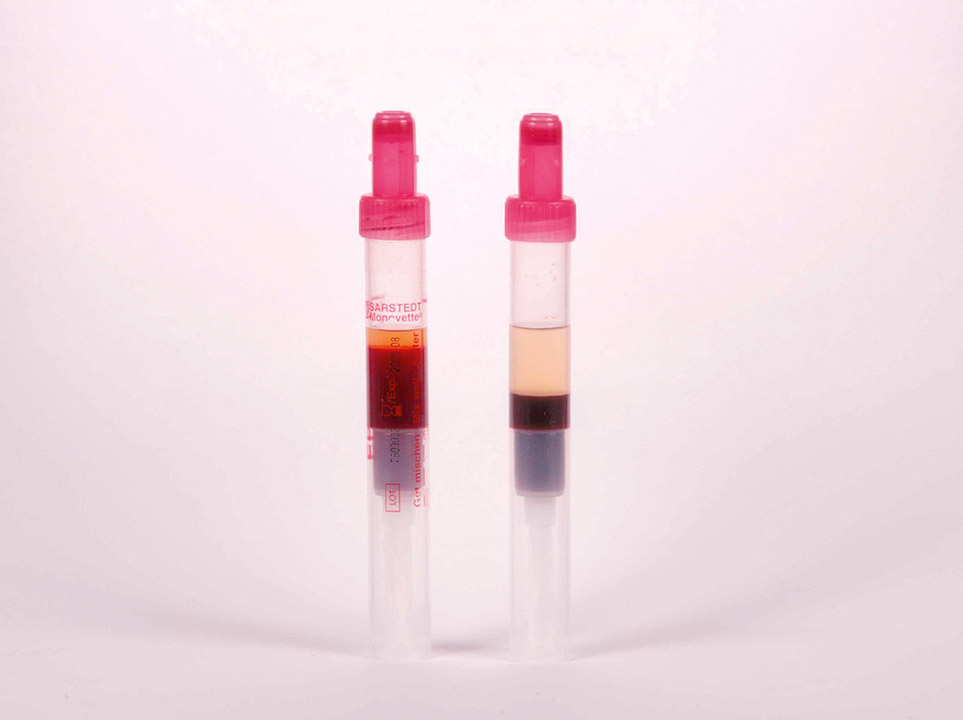
Pronounced erythrocytosis (polyglobulia) can often already be recognised after sedimentation of the red blood cells. Left tube: haematocrit 82%, right tube: haematocrit 39%.
<p>Pronounced erythrocytosis (polyglobulia) can often already be recognised after sedimentation of the red blood cells. Left tube: haematocrit 82%, right tube: haematocrit 39%.</p>
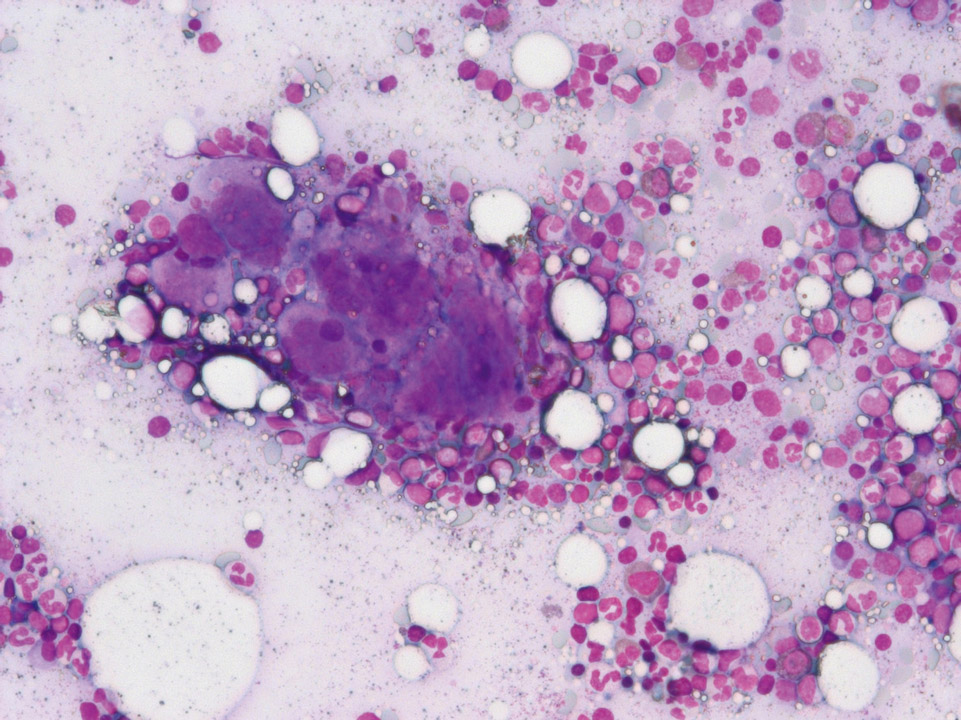
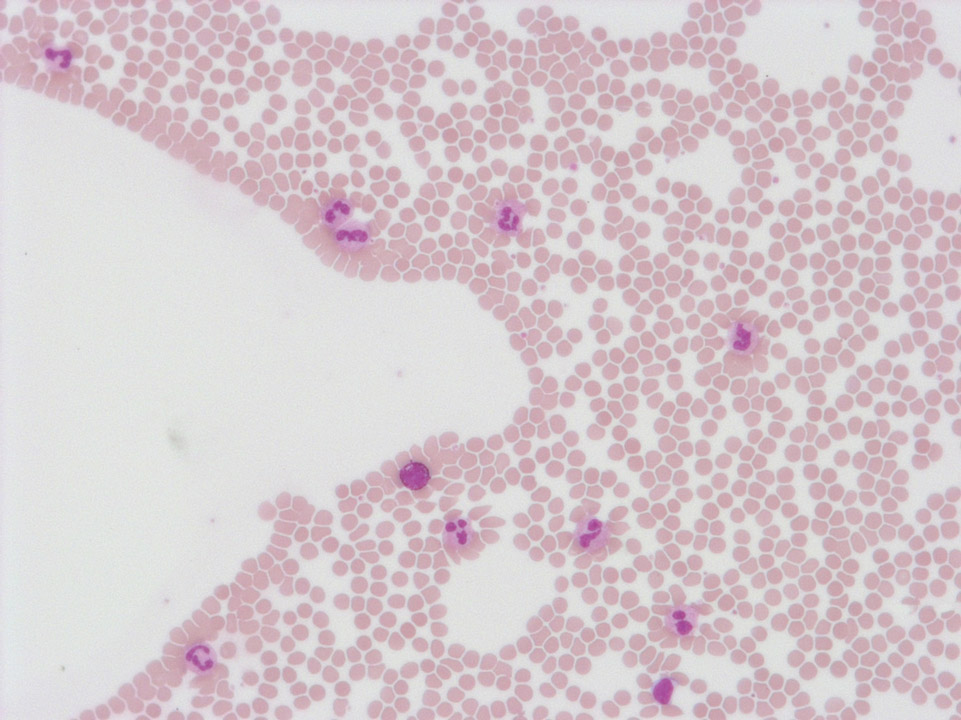
The bone marrow cytology (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with ET shows a clear increase in exceptionally large megakaryocytes.
<p>The bone marrow cytology (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with ET shows a clear increase in exceptionally large megakaryocytes.</p>
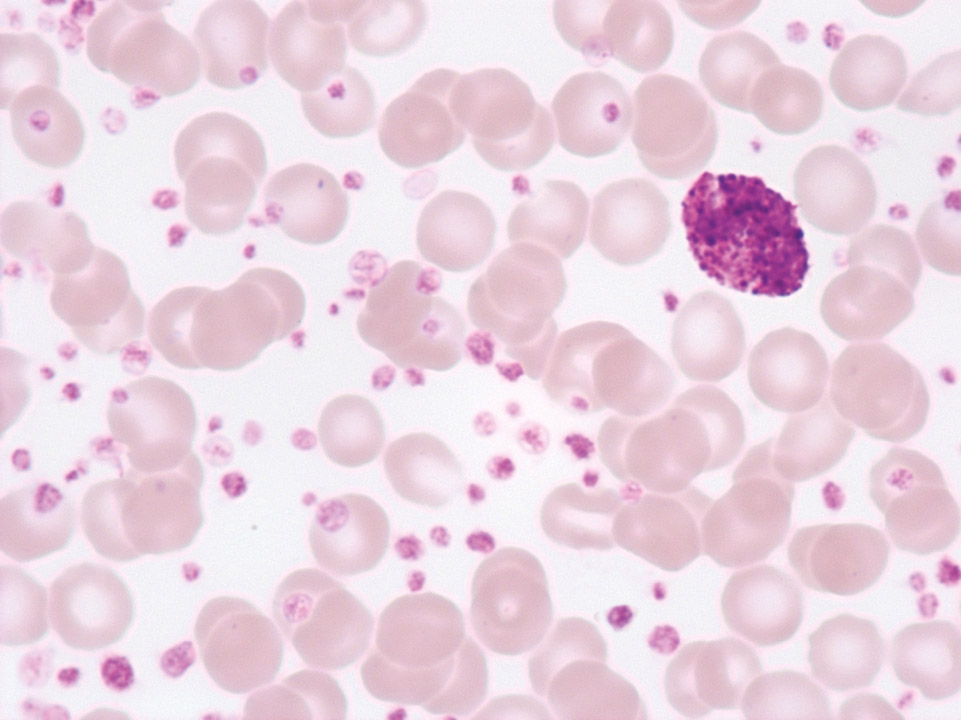
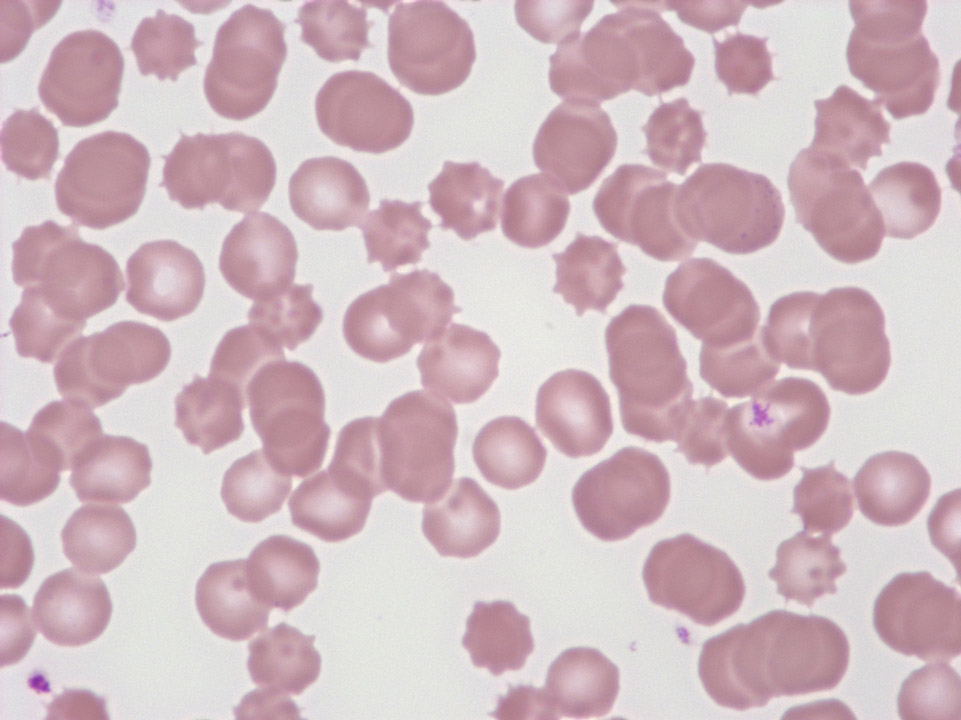
Extreme thrombocytosis (3,400,000/μL) in chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML, bcr-abl+); on the right a basophilic granulocyte.
<p>Extreme thrombocytosis (3,400,000/μL) in chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML, bcr-abl+); on the right a basophilic granulocyte.</p>